If Income Rises The Budget Constraint
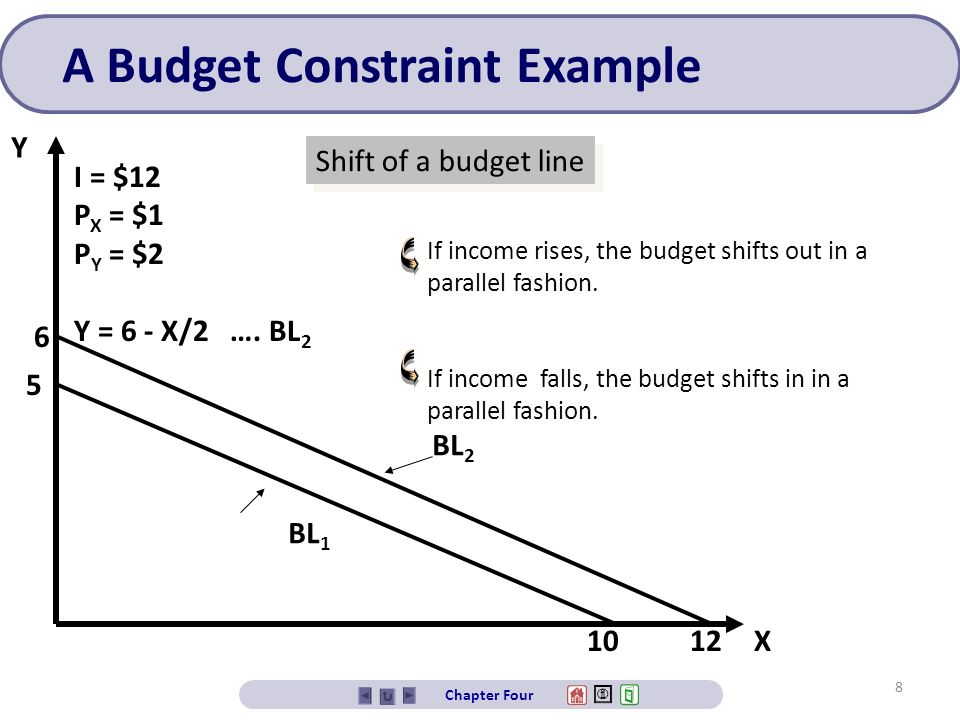
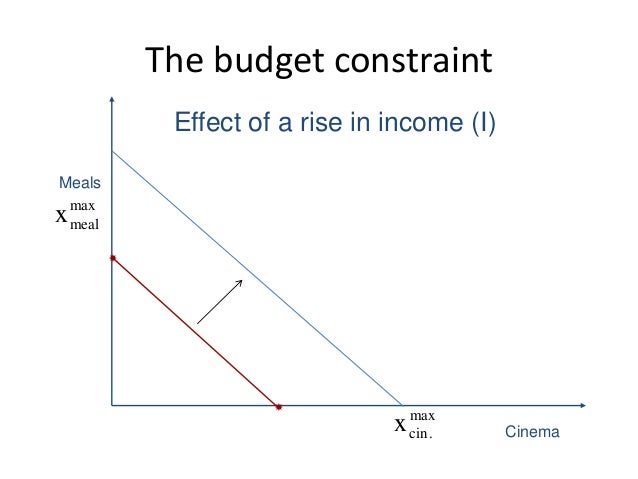
The rise in income shifts the budget constraint out from BC 1 to BC 2. Leave a Reply Cancel reply.
O PxPy O MUYMUX O PyPX O MUXMUY The income elasticity of a good is 3.

If income rises the budget constraint. What does the budget constraint framework suggest when income rises. Here the consumer buys more pizza and more Pepsi. The slope of the budget constraint MUST be negative and is.
The budget constraint framework suggest that when income or price changes a range of responses are possible. If both goods are normal goods the consumer responds to the increase in income by buying more of both of them. Therefore points between the budget constraint and the origin are points where the consumer is not spending all of their income ie.
The new combinations of products that maximise utility can be identified. Select the correct answer below. Your email address will not be published.
As a result the budget line would have a rightward parallel shift from L 1 M 1 to a new position like L 2 M 2. Many government transfer programs impose additional nonlinearities by altering this tax rate by discrete. An Increase in Income.
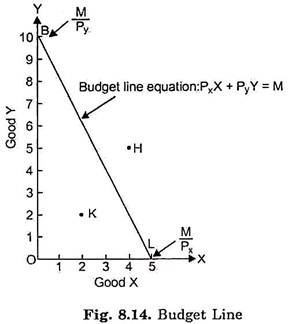
This equation states that the consumer cannot spend more than his income but can spend less. With cheese on the horizontal axis and wine on the vertical axis the budget constraint has a slope of - 1000500 -2. When the consumers income rises the budget constraint shifts out.
C shift in parallel to the old one. Along the budget constraint the prices of the two goods remain the same so the ratio of the prices doesnt change. If a consumer buys less of a good when his or her income rises the good is called an inferior good.
Constraints because transfer benefits are taxed in the sense of a negative income tax as income rises and because that tax rate falls to zero at the kink point where an individual or family loses eligibility for the benefit altogether. If the money the consumer has to spend on the two goods his income is given as I then the budget constraint is. When income rises households will demand a higher quantity of normal goods but a lower quantity of inferior goods.
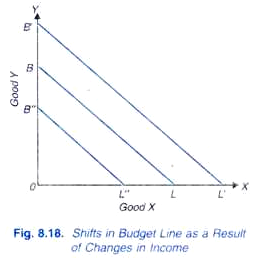
Demand falls as income rises. If a Households Income Rises by 30 Its Budget Constraint. Conversely if the money income of the consumer decreases prices remaining constant the budget line would have a parallel shift to the left.
The budget constraint represents all of the points where the consumer is spending all of their income. Plotting the budget constraint is a fairly simple process. This rightward or leftward parallel shift of the budget line is known as shift of the budget line.
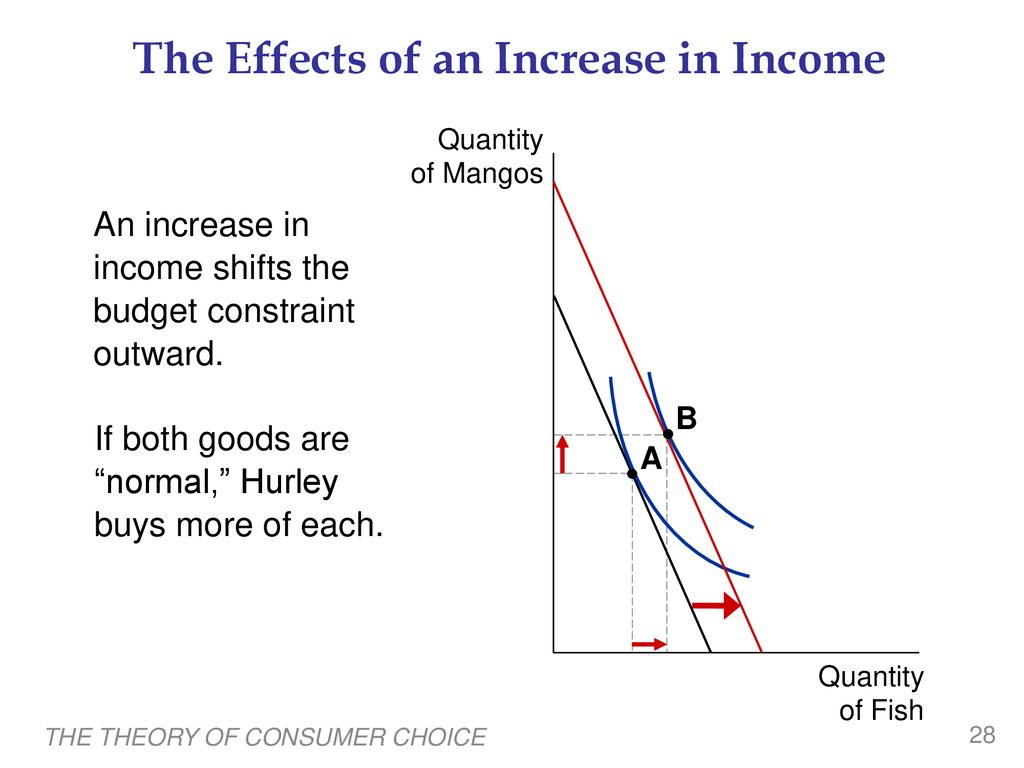
Figure 2 shows the effect of an increase in income. Normal versus Inferior Goods If a consumer buys more of a good when his or her income rises the good is called a normal good. Cost of living adjustement.
When income rises households will demand a higher quantity of normal goods but a. But José like all of us faces a budget constraint. The budget constraint line shows the various combinations of goods that it is possible to buy given a certain level of income.
32latexP_AAP_BBgeq Ilatex Note the inequality. Each point on the budget line has to exhaust all 56 of Josés budget. Is spending less than their income and points farther from the origin than the budget constraint are unaffordable to the consumer.
T-shirts cost 14 and movies cost 7. Total consumption in dollars at all points on the budget line equals total income. Y1 pc1 C1 pf1 F1.
If Product A is plotted on y-axis and Product B on x-axis the budge line touches y-axis at a point at which all budget is spent on Product A and it touches x-axis at a point at which only Product B is. If both wine and cheese are normal goods consumption of both will increase. If consumer income rises consumes less of good X.
B pivot at the Y-intercept. The budget constraint framework suggest that when income or price changes a range of responses are possible. However the marginal utility of the two goods changes with the quantities consumed.
Buy if she bought only wine. When an increase in income shifts the budget constraint outward. Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand.
An increase in income shifts the budget line out parallel. The income effect is a change in income that affects the number of goods or services individuals will demand or purchase. CPI in the second year is the cost of buying the first years bundle in.
Learn more about its definition examples and the income effect on prices. CPI in first year is the cost of buying the market basket of food F and clothing C that was actually purchased that year. The good is a necessity and when income rises by 1 quantity demanded rises by 3.
Answer to what does the budget constraint framework suggest when income rises. When income rises households will demand a higher quantity of normal goods but a lower quantity of inferior goods. A budget line is also called a budget constraint because it limits total consumption possibility of a consumer.
1 and x 2 increase as income rises x 1 and x 2 are normal goods Quantity of x 1 Quantity of x 2 C U 3 B U 2 A U 1 As income rises the individual chooses to consume more x 1 and x 2. If this is a normal good an increase in income increases the quantity demanded. With income of 3000 and the price of wine 3 a glass she could buy 1000 glasses of wine.
An increase in income shifts the budget constraint out in a parallel fashion Since p 1 p 2 does not change the optimal MRS will stay. Select the correct answer below. What does the budget constraint framework suggest when income rises.
6 Increase in. New budget constraint 1. The budget constraint framework suggest that when income or price changes a range of responses are possible.
José has a total of 56 to spend. If cheese is an inferior good the increase in income causes the consumption of cheese to decline as shown in Figure 3. When income rises households will demand a higher quantity of normal goods but a lower quantity of inferior goods.
The budget constraint framework suggest that when income or price changes a range of responses are possible. If José had unlimited income or if goods were free then he could consume without limit. What does the budget constraint framework suggest when income rises.
If a households income rises by 30 its budget constraint will A shift out parallel to the old one.

Income Changes And Consumption Choices Microeconomics
Economics A Change In The Price Of A Good And The Budget Line
Budget Line Notes On Budget Line Space Changes And Slope
Concept Of Budget Line With Diagram Consumer S Equilibrium Economics
The Theory Of Consumer Choice Ppt Download
What Happens To The Budget Line When The Price Changes Quora

Consumer Choice Budget Line Changes Economics Tutorials

Chapter 4 Utility Maximization And Choice Consumer Behavior

How The Budget Line Changes Microeconomics Hayden Economics
(184).jpg)
A Consumer Choice In Microeconomics Quiz Proprofs Quiz
Chapter Four Consumer Choice Chapter Four Chapter Four Consumer Choice Chapter Four Ppt Video Online Download

The Theory Of Consumer Choice Budget Line Constraint

How Changes In Income And Prices Affect Consumption Choices Os Microeconomics 2e


Posting Komentar untuk "If Income Rises The Budget Constraint"